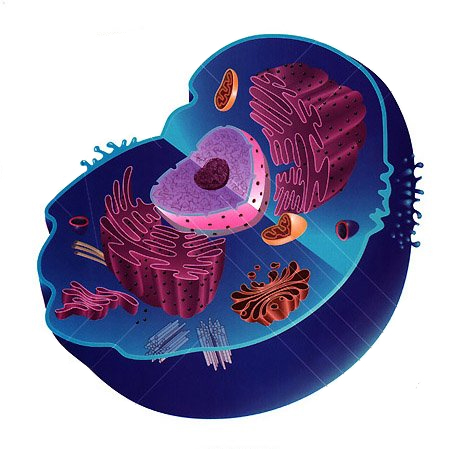
Definition Animal cells are the fundamental unit of life in Animalia creatures. They are eukaryotic cells, which means they include a genuine nucleus and specialized components known as organelles that perform certain activities. Animal cells lack organelles unique to plants, such as cell walls, which sustain the plant cell, or chloroplasts, the organelle responsible for photosynthesis.
The numerous components of the cell are referred to as Organelles. Organelles are subunits of the cell that execute their own sub tasks to assist the cell in performing effectively.
I hope you gained valuable knowledge about cell structure from our plant and animal cell photographs. Share what you learnt today with a friend, and you'll remember it as a token of thanks!
Animals have a variety of complex organelles that assist them in forming some fairly mind-boggling structures such as bones, muscles, and nerves â these organelles, in fact, are what enable animals to create empires. However, mammals lack one organelle: the chloroplast, which enables plants to photosynthesize, or convert light into glucose molecules. Thus, whatever green on a plant â the leaf, the stem, or even the peel of an unripe banana â originates from the chloroplasts in its cells. Converting light to food – give it a try, animals! A typical chloroplast-containing plant cell is shown as follows:
Rat oviduct cilia and mucous cells. Getty Images / Micro Discovery Cells are the basic living units in the hierarchical framework of life. Animal creatures may be billions of cells in size. There are hundreds of distinct cell kinds in the human body. These cells come in a variety of forms and sizes, and their architecture is optimized for their purpose. For instance, brain cells, or neurons, in the body have a radically different form and function than red blood cells. Nerve cells are responsible for the transmission of electrical impulses throughout the nervous system. They are elongated and thin, with protruding projections that connect to other nerve cells in order to conduct and transmit nerve impulses. Red blood cells' primary function is to carry oxygen to bodily cells. Their compact, flexible disc form allows them to go through microscopic blood channels, delivering oxygen to organs and tissues.