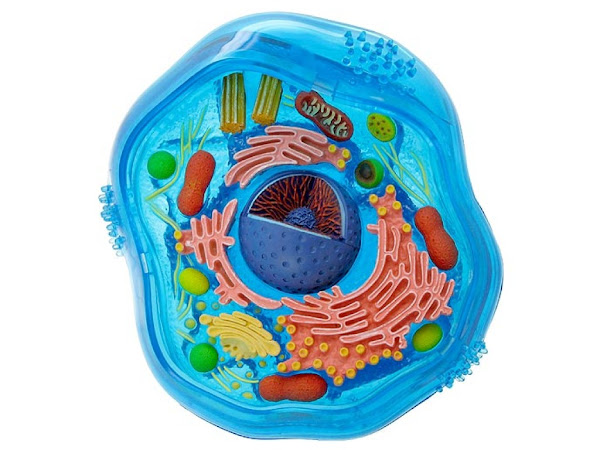
A plant cell's structure Plant cells are eukaryotic cells found in green plants, the kingdom Plantae's photosynthetic eukaryotes. Their distinguishing characteristics include primary cell walls composed of cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectin, the presence of plastids capable of photosynthesis and starch storage, a large vacuole that regulates turgor pressure, the absence of flagella or centrioles, except in gametes, and a unique method of cell division that involves the formation of a cell plate or phragmoplast that separates the new daughter cells.
Currently, the majority of super-resolution microscopy findings in plant cell research are centered in the disciplines of research groups that have access to super-resolution microscopes. However, it is projected that applications will expand greatly in the future owing to super-wide resolution's relevance to biological specimen analysis, such that super-resolution microscopy will become a routine method in plant cell research as well. This progress will be pushed further by optimizing and merging current super-resolution technologies. SIM, in particular, has the potential to be applied to the area of live cell imaging. Additionally, SIM approaches are being developed to improve on the twofold gain in resolution obtained so far.
Plasmodesmata - Plasmodesmata are tiny tubes that link individual plant cells, acting as living bridges between them.
Plasma Membrane - Every live cell has a plasma membrane that surrounds its contents. The membrane is the innermost layer of protection in prokaryotes and plants, surrounded by a hard cell wall. Additionally, these membranes govern the flow of chemicals into and out of cells.
Acquaint yourself with the many agents of pollination. Additionally, this page offers instances of each kind of pollination agent with accompanying photographs. Additionally, this page discusses how these agents pollinate flowers, how they choose flowers to pollinate, and the whole process of pollination. Three Various Ecosystem Types Ecosystems are classified into three types: natural ecosystems, man-made ecosystems, and microecosystems. This page discusses the properties of ecosystems, their subclasses, and instances with pictures.